Development Environment Setup#
Follow the instructions below to set up a development environment (IDE) on your Windows, Mac or Linux PC. Stb-tester’s IDE integration provides the following features:
Auto-complete for Stb-tester APIs:
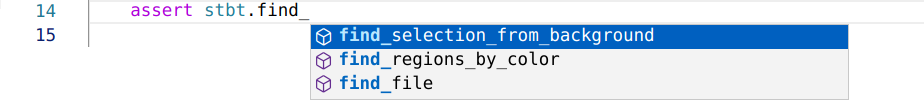
API documentation in the IDE:
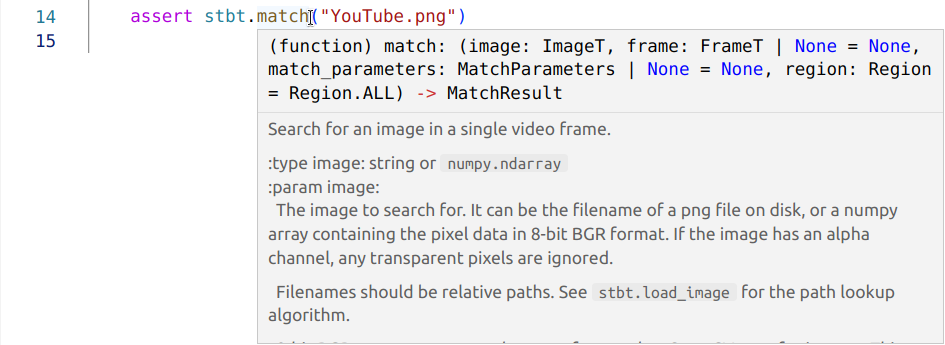
Pylint checks in the IDE, including custom checks for the Stb-tester APIs:
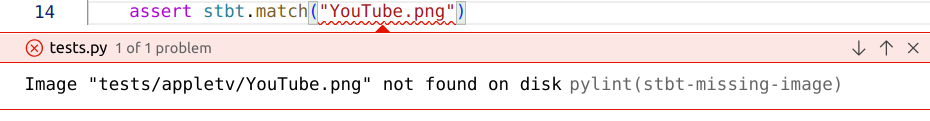
Run tests directly from the IDE, without having to commit or push:
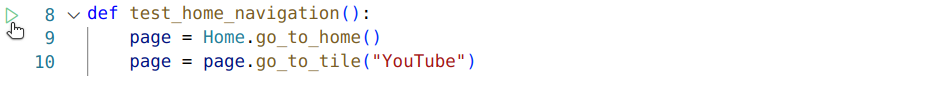
Note: The tests won’t execute directly on your PC; this will sync your code to the Stb-tester Portal and run your test on an Stb-tester Node.
Automatically sync your code to the portal when you press “Save” (without having to commit or push) for instant feedback in the Object Repository during test-script development. This doesn’t affect your local git checkout (it doesn’t make any commits on your checked-out branch) so after you have tested your changes & got them working, you still need to do “git commit” and “git push” to make it official.
We recommend VS Code. We also provide instructions for PyCharm, but this configuration is less well tested.
Installation and configuration instructions: